Choosing the right heating system for your home is crucial for maintaining comfort and efficiency, especially during the colder months. With so many types of heating systems available, it’s essential to understand their differences, benefits, and drawbacks to make an informed decision. The best system for you will depend on factors such as your home’s size, energy efficiency preferences, climate, and budget.
In this guide, we’ll explore the various types of heating systems, their functions, and which might be the best fit for your home.
1. Forced Air Heating System
What Is a Forced Air Heating System?
A forced air heating system uses a furnace to heat air and then blows it through ducts and vents to warm the entire home. This system is one of the most common and widely used heating methods. It works with natural gas, oil, or electricity, providing flexibility depending on the fuel source.
Advantages of Forced Air Heating
- Quick Heating: Forced air systems are efficient at quickly raising the temperature in your home.
- Air Circulation: The system also provides air circulation, which can help maintain consistent temperatures.
- Additional Features: Forced air systems can be integrated with air conditioning systems, making it a year-round solution.
Disadvantages of Forced Air Heating
- Air Quality: The movement of air can stir up dust and allergens, affecting indoor air quality.
- Noise: Some systems can be noisy, especially when the blower is in operation.
- Energy Loss: If ducts are poorly insulated or have leaks, energy loss can occur, reducing efficiency.
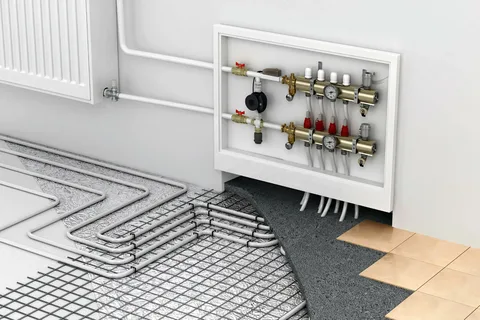
2. Radiant Heating System
What Is a Radiant Heating System?
Radiant heating systems work by warming the surfaces in a room, such as floors, walls, or ceilings. This type of system uses either electric coils or hydronic (water-based) systems. With hydronic systems, warm water circulates through pipes beneath the floor, while electric radiant heating uses cables or mats beneath the floor surface.
Advantages of Radiant Heating
- Comfort: Radiant heating provides consistent, even warmth throughout a room, avoiding cold spots.
- Energy Efficiency: Since the system directly heats surfaces, it can be more energy-efficient than forced air systems.
- Silent Operation: Radiant heating is virtually silent, which adds to its appeal in terms of comfort and convenience.
Disadvantages of Radiant Heating
- High Installation Costs: Radiant heating systems, particularly hydronic systems, can be expensive to install.
- Slow Heating Time: Unlike forced air systems, radiant heating can take longer to raise the temperature of a room.
- Difficult to Retrofit: It may be difficult to install radiant heating in existing homes, particularly with hydronic systems.
3. Boiler Heating System (Hydronic Heating)
What Is a Boiler Heating System?
A boiler heating system uses a boiler to heat water, which is then pumped through pipes to radiators, baseboard heaters, or underfloor heating. Boilers can use gas, oil, or electricity to generate heat. This system is often used in colder climates where consistent and efficient heat is needed.
Advantages of Boiler Heating
- Even Heating: Boilers provide a steady, consistent heat, making them ideal for larger homes or colder climates.
- Quiet Operation: Boilers are quieter compared to forced air systems, as there are no noisy fans or blowers.
- Energy Efficient: When well-maintained, boiler systems can be very energy-efficient, particularly when paired with radiant heating.
Disadvantages of Boiler Heating
- Expensive Installation: Installing a boiler system can be costly, especially in homes that were not previously equipped with such systems.
- Slow Heat Distribution: Boiler systems can take longer to heat up compared to forced air systems.
- Space Requirements: Boilers require adequate space for installation, which may be a challenge in smaller homes.
4. Heat Pump System
What Is a Heat Pump System?
A heat pump system is a versatile option that can both heat and cool your home. It works by transferring heat from one place to another. In winter, it extracts heat from the outside air or ground and brings it inside. In summer, it does the reverse, acting as an air conditioner. Heat pumps are energy-efficient and can operate in various climates.
Advantages of Heat Pumps
- Dual Function: Heat pumps provide both heating and cooling, making them a great all-season solution.
- Energy Efficiency: Heat pumps are highly energy-efficient, especially in mild climates.
- Low Operating Costs: Heat pumps generally have lower operating costs than other heating systems, such as electric resistance heaters.
Disadvantages of Heat Pumps
- Limited Efficiency in Extreme Cold: In extremely cold climates, heat pumps may struggle to provide adequate heating.
- Higher Initial Cost: The initial installation cost of a heat pump can be higher than traditional heating systems.
- Maintenance Requirements: Heat pumps need regular maintenance to keep them running efficiently, especially in regions with extreme temperatures.
5. Electric Heating System
What Is an Electric Heating System?
Electric heating systems can take several forms, including baseboard heaters, space heaters, and electric furnaces. These systems rely on electricity to generate heat, which is then distributed through convection or radiation.
Advantages of Electric Heating
- Low Installation Costs: Electric heating systems are often less expensive to install compared to other systems like boilers or forced air.
- No Need for Ductwork: Electric heaters do not require ducts, making them ideal for homes without existing ductwork or for supplemental heating in specific rooms.
- Simple Operation: Electric heating is easy to use and does not require complex maintenance.
Disadvantages of Electric Heating
- Higher Operating Costs: Electricity tends to be more expensive than other energy sources, so electric heating can result in higher utility bills.
- Limited Coverage: Electric heating is often better suited for small spaces or as a supplementary heating source.
- Environmental Impact: If the electricity comes from non-renewable sources, electric heating systems may have a higher environmental impact.
6. Geothermal Heating System
What Is a Geothermal Heating System?
Geothermal heating systems use the earth’s natural heat to warm your home. A heat pump is installed to transfer heat from the ground into your home. Geothermal systems use underground pipes filled with fluid to exchange heat with the earth, making it a highly energy-efficient option.
Advantages of Geothermal Heating
- Energy Efficient: Geothermal systems are incredibly energy-efficient because the earth’s temperature remains consistent year-round.
- Low Operating Costs: Once installed, geothermal systems have very low operating costs due to their efficiency.
- Environmentally Friendly: Geothermal heating systems produce little to no greenhouse gas emissions, making them an environmentally friendly choice.
Disadvantages of Geothermal Heating
- High Installation Costs: Geothermal systems can have a high upfront cost due to the installation of ground loops and heat pumps.
- Space Requirements: The system requires significant space for the installation of ground loops, making it less suitable for smaller properties or those in urban areas.
- Long Payback Period: Although the system is cost-effective in the long run, it may take several years to recoup the initial installation costs.
7. Pellet Stove Heating System
What Is a Pellet Stove?
A pellet stove is a type of heating system that uses compressed wood pellets as fuel. The stove burns the pellets to create heat, which is then distributed throughout the home. This type of system is often used for supplemental heating in homes or for heating specific rooms.
Advantages of Pellet Stoves
- Eco-Friendly: Pellet stoves use renewable biomass fuels, making them a more environmentally friendly option compared to fossil fuel-based systems.
- Cost-Effective: Pellet stoves are cheaper to operate than electric or oil heating systems.
- Efficient Heating: They provide effective and direct heat, making them ideal for smaller spaces or as a supplemental heat source.
Disadvantages of Pellet Stoves
- Maintenance Needs: Pellet stoves require regular cleaning and maintenance to keep them functioning properly.
- Fuel Supply: Pellet stoves require a consistent supply of pellets, which may need to be purchased and stored.
- Limited Heating Area: Pellet stoves are more suitable for heating specific areas of a home rather than an entire house.
Conclusion
Choosing the right heating system for your home is a critical decision that impacts both comfort and energy costs. From forced air systems to geothermal heating, each system has its own advantages and challenges. Understanding these options and assessing your home’s needs will help you make an informed decision and ensure that you choose the most efficient, cost-effective, and comfortable solution for your space.
FAQs
1. What is the most energy-efficient heating system?
Geothermal heating systems are considered one of the most energy-efficient options, as they use the earth’s constant temperature to heat homes. Heat pumps are also highly efficient, particularly in mild climates.
2. Which heating system is best for large homes?
For large homes, a forced air heating system or a boiler system is often the best option. These systems can provide the necessary heat output to efficiently warm larger spaces.
3. Are there any heating systems that can cool my home as well?
Yes, heat pumps can both heat and cool your home, making them a versatile year-round option for temperature control.
4. How do I know which heating system is right for my home?
The right heating system for your home depends on several factors, including the size of your home, your climate, your budget, and your energy efficiency preferences. Consider consulting with a professional to determine which system would work best for your needs.
5. Can I switch from one heating system to another?
Switching from one type of heating system to another is possible but may require significant modifications, such as installing new ductwork or plumbing. A professional HVAC contractor can help you assess the feasibility of making such a change.


